Static Lateral Pile Load Test

STATIC LATERAL PILE LOAD TEST AS PER IS 2911 PART-4 2013
A lateral pile load test is a field test conducted on piles to assess their ability to withstand sideways forces, like those caused by wind, seismic activity, or earth pressure. It determines the pile’s lateral load-carrying capacity and deformation characteristics. This test helps engineers ensure the stability of structures relying on these piles, especially in the face of horizontal forces.
Purpose
- Determine lateral load capacity: The test aims to find the maximum sideways load the pile can safely handle before significant deformation or failure.
- Evaluate pile behavior: It examines the pile's deflection, stiffness, and how it responds to lateral loads.
- Ensure structural stability: By understanding the pile's behavior under lateral loads, engineers can design structures that can withstand these forces.
Process
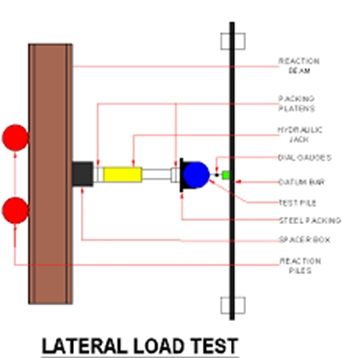
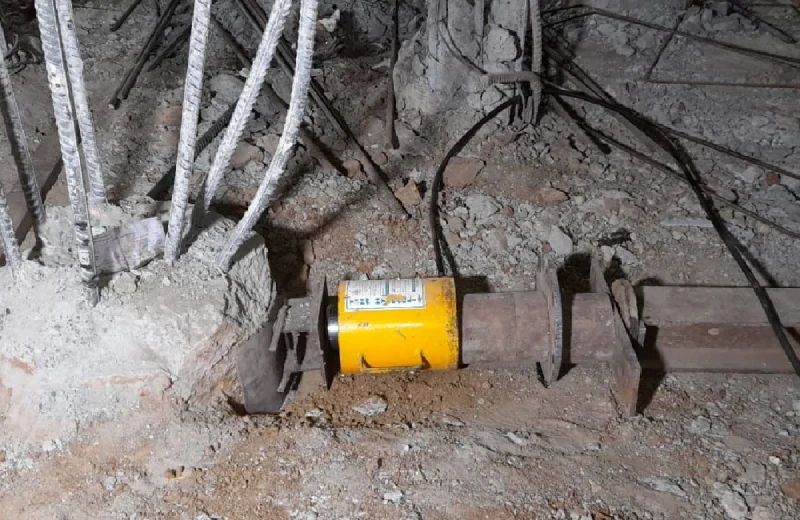
- Test Setup: A horizontal force is applied to the pile, typically using a hydraulic jack, and its displacement is monitored.
- Load Application: Incremental loads are applied, and the pile's response is observed.
- Displacement Measurement: Dial gauges or other instruments are used to measure the lateral displacement of the pile head and other points along its length.
- Data Analysis: The load-displacement data is analyzed to determine the pile's lateral resistance and identify its safe load-carrying capacity.
Factors Affecting Lateral Pile Load Test
- Pile Type: Different pile types (e.g., concrete, steel, timber) have varying lateral load-bearing capacities.
- Soil Conditions: The type of soil and its density influence how the pile interacts with the surrounding ground.
- Pile Length and Diameter: These dimensions affect the pile's stiffness and its resistance to lateral forces.
- Load Application Method: The method of applying the horizontal load can impact the test results.