Low Strain Integrity Test

LOW STRAIN INTEGRITY TEST ON PILE AS PER IS 14893 2021
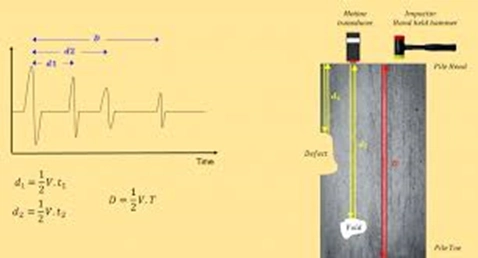
Pile Integrity Testing (PIT) is a non-destructive method used to assess the quality and integrity of piles, particularly deep foundations. It involves applying low-strain impacts to the pile and analyzing the resulting stress waves to identify any anomalies or defects. PIT is valuable for evaluating pile length, cross-sectional area, material consistency, and potential issues like voids or cracks.
Here’s a more detailed explanation. What it is:
- PIT, also known as low-strain impact integrity testing, uses a light-weight hammer or impact device to create a stress wave that travels down the pile.
- This wave is reflected back from the pile toe and any changes in impedance (like changes in pile material or cross-section) along the way.
- Accelerometers (sensors) on the pile head record the reflected wave, and the data is analyzed to determine the pile’s condition.
How it works:
- Impact: A light hammer is used to strike the pile head, generating a compressive stress wave.
- Reflection: The wave travels through the pile and is reflected back from the pile toe and any anomalies (like voids, cracks, or changes in material).
- Recording: Accelerometers, attached to the pile head, record the reflected wave's velocity and sometimes force.
- Analysis: The collected data is analyzed to identify changes in the wave's characteristics, indicating potential issues with the pile.
What it detects:
- Pile length: The time it takes for the stress wave to travel to the toe and back can be used to estimate the pile length.
- Cross-sectional area: Changes in the wave's characteristics can indicate variations in the pile's diameter or shape.
- Material consistency: Anomalies can reveal issues like voids, cracks, or segregation in the concrete mix.
- Continuity: PIT can detect major voids and cracks that may compromise the pile's integrity.
Benefits:
- Non-destructive: The test doesn't damage the pile and can be performed on existing or new piles.
- Quick and efficient: PIT is relatively quick and can be used to test multiple piles in a single day.
- Cost-effective: Compared to destructive testing methods, PIT is a cost-effective way to assess pile integrity.
- Versatile: PIT can be used on various pile types, including cast-in-place concrete, driven concrete, and timber piles.
Limitations:
- Limited to concrete piles: PIT works best on solid concrete piles and has limited application to steel pipe piles and H-piles.
- Interpretation requires experience: Analyzing PIT data can be challenging and requires expertise to accurately identify potential issues.
- Effect of soil conditions: Soil conditions can affect the stress wave's propagation and interpretation of results.