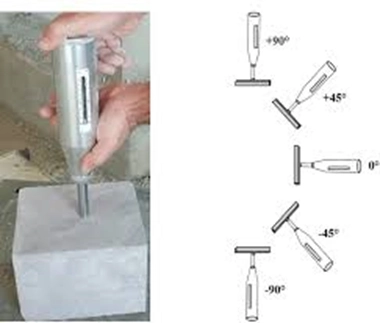
Rebound Hammer Test
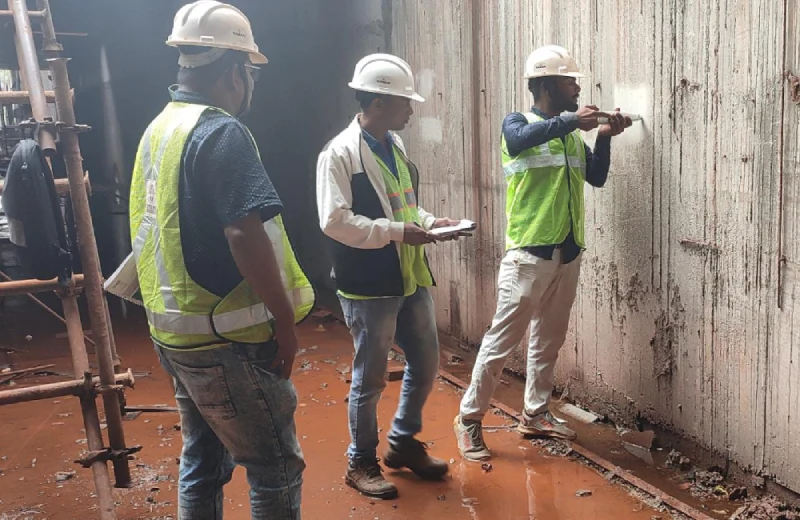

REBOUND HAMMER TEST AS PER IS 516 PART-5 SEC-4 2020
The rebound hammer test is a non-destructive method used to estimate the compressive strength of concrete by measuring the surface hardness. It involves striking the concrete surface with a hammer and measuring the rebound of the hammer’s mass. The rebound value, or rebound index, is then used to determine an approximate compressive strength, often with the aid of a calibration chart.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
Principle:
- The rebound hammer operates on the principle that the rebound of an elastic mass depends on the hardness of the surface it strikes. A spring-controlled mass within the hammer is propelled against the concrete surface, and the rebound distance is measured.
Procedure:
- Preparation: Ensure the concrete surface is smooth, clean, and dry.
- Impact: The hammer's plunger is pressed against the concrete surface at a right angle.
- Measurement: The rebound of the hammer's mass is measured on a graduated scale, resulting in the rebound number or index.
- Calculation: The rebound index is converted to an approximate compressive strength using a calibration chart or formula provided by the manufacturer, according to Virtual Labs.