High Strain Dynamic Load Test

HIGH STRAIN DYNAMIC LOAD TEST AS PER ASTM D4945
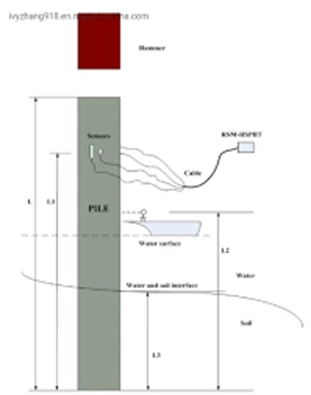
High Strain Dynamic Load Testing (HSDLT) is a geotechnical testing method used to evaluate the bearing capacity and integrity of deep foundations like piles and drilled shafts. It involves applying a dynamic load, typically from a falling weight, and analyzing the resulting stresses and accelerations within the foundation. This method is faster and more cost-effective than traditional static load tests, offering valuable insights into the foundation’s performance.
Here’s a more detailed explanation. What it is:
- HSDLT is a dynamic test that applies a rapid, impact load to a foundation element (like a pile).
- It uses specialized equipment, such as a pile driving analyzer (PDA), to measure the force and velocity response of the pile during the impact.
- The collected data is then analyzed to determine the pile’s bearing capacity, integrity, and soil resistance characteristics.
How it's done:
- Instrumentation: Strain transducers and accelerometers are attached to the pile to measure the force and velocity response to the impact.
- Impact: A falling weight or hammer is used to impact the pile head, creating a dynamic load.
- Data Acquisition: The PDA records the force and velocity time history from the strain transducers and accelerometers.
- Analysis: The recorded data is analyzed using wave equation analysis (e.g., CAPWAP) to determine the pile's bearing capacity and other properties.
Advantages of HSDLT:
- Faster and more cost-effective: HSDLT is typically faster and less expensive than static load tests.
- More tests can be conducted: The dynamic nature of the test allows for more testing in a given time.
- Space requirements: HSDLT generally requires less space than static load tests.
- Capacity confirmation: It can confirm the capacity of foundations even at large loads.
- Provides detailed information: HSDLT provides information on resistance distribution, pile integrity, and load-movement characteristics.